Transforming Surgery: The Expanding Role of Robotics in Healthcare
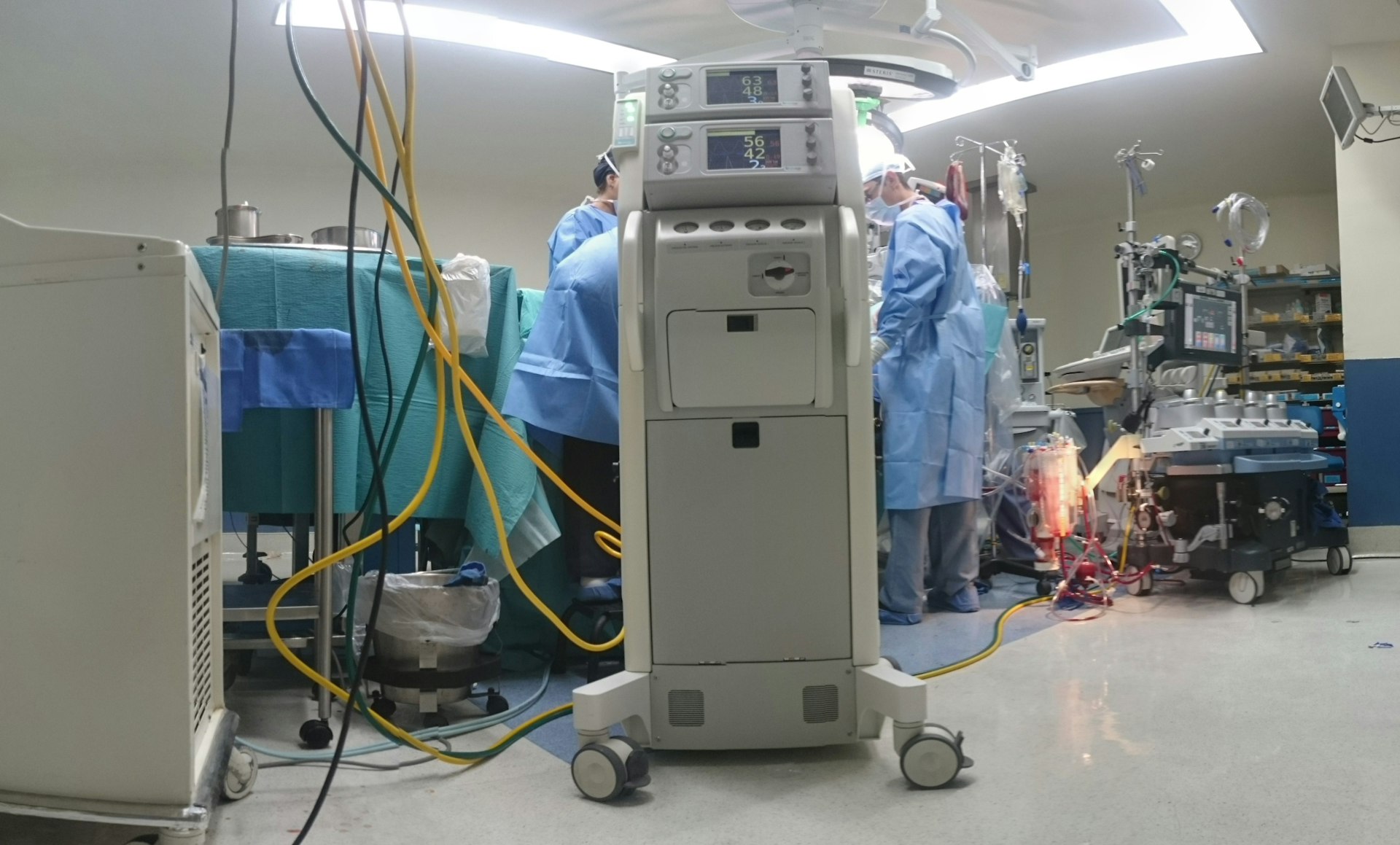

Photo by Natanael Melchor on Unsplash
Introduction
Robotics has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare surgery, offering substantial improvements in precision, safety, and patient recovery. As robotic-assisted procedures become more widely available, both patients and healthcare professionals are seeking clear, actionable guidance on the benefits, applications, and pathways to access these advanced surgical options.
Core Benefits of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgical systems bring several distinct advantages to the operating room. Precision is a primary benefit; robotic arms can perform delicate maneuvers with accuracy beyond the capability of the human hand, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient outcomes [1] . Enhanced dexterity is another key factor-robotic arms can rotate 360 degrees, mimicking and extending the surgeon’s natural movements while minimizing tremors. This is especially valuable for complex tasks in confined anatomical spaces.
Three-dimensional visualization provided by advanced robotic systems offers surgeons superior depth perception and spatial awareness, further contributing to safe, accurate procedures [1] . In addition, the ergonomic design of robotic consoles allows surgeons to operate from a seated position, reducing physical strain and fatigue during lengthy surgeries, thus maintaining optimal performance throughout [1] .

Photo by Piron Guillaume on Unsplash
Clinical Applications of Robotic Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is now used across a broad spectrum of specialties. In gastrointestinal surgery , robots assist with procedures such as cholecystectomy, gastric bypass, and colectomy. Urologic surgeries -especially radical prostatectomy-have seen widespread adoption of robotic systems in the United States and Europe. In gynecology , robotic hysterectomy and microsurgical procedures are increasingly common [2] .
Cardiothoracic surgeons employ robotic platforms for coronary bypass and valve repairs, reducing the need for large incisions and leading to shorter hospital stays. Pediatric and oncologic surgeries, including tumor removals and congenital heart repairs, are also benefiting from robotic technology [2] . With continuous advancements, the reach of robotic surgery is expanding into new, highly specialized procedures [4] .
Technology in Practice: How Robotics Improves Outcomes
Robots enhance intraoperative consistency by holding instruments steady and precisely on target, as seen in complex spinal surgeries, minimizing human error and reducing overall procedure times [3] . When integrated with navigation systems, robots help align instruments accurately with patient anatomy, critical for procedures like scoliosis correction.
These systems also support the surgical team by automating repetitive or ergonomically challenging tasks, allowing the surgeon to focus on complex decision-making. As a result, patients typically experience less operative trauma, fewer complications, and faster recoveries [4] . For example, minimally invasive robotic cardiac procedures can reduce recovery times and lower the risk of complications compared to traditional open surgeries [5] .
Accessing Robotic-Assisted Surgery
If you or a loved one is considering robotic-assisted surgery, here are steps you can take:
- Consult with your healthcare provider: Discuss your condition with your primary care physician or specialist. Ask if robotic-assisted surgery is appropriate for your case and what benefits or risks may apply.
- Research hospitals and surgical centers: Many major hospitals and academic medical centers now offer robotic surgery. You can search for facilities with established robotic surgery programs or consult resources from organizations such as the American Hospital Association.
- Verify surgeon expertise: Ask about your surgeon’s experience with robotic procedures, including their certification and the number of surgeries performed.
- Insurance coverage: Contact your health insurance provider to determine if robotic procedures are covered under your plan. Be prepared to request pre-authorization or provide documentation of medical necessity.
- Seek second opinions: Consider consulting another specialist to confirm the appropriateness of robotic surgery for your situation.
You may also inquire about clinical trials or research studies at academic medical centers for access to the latest robotic technologies. For official contact information, use hospital websites or search for “robotic surgery program” along with the hospital or health system of interest.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, robotic surgery presents several challenges. The cost of acquiring and maintaining robotic systems can be significant, and not all hospitals may offer these services, especially in rural or under-resourced areas. Patients may encounter higher out-of-pocket costs depending on their insurance coverage.
Robotic systems also require specialized training, and there can be a learning curve for surgeons new to the technology. Hospitals typically address this with structured training programs and proctoring by experienced practitioners. Patients are encouraged to verify their surgeon’s credentials and inquire about the volume of robotic procedures performed at the facility.
While robotic platforms reduce many technical limitations, they are not suitable for all patients or procedures. Your healthcare team will evaluate your medical history, anatomy, and specific surgical needs to determine the best approach.
Recent Innovations and Future Directions
The field of robotic surgery is rapidly evolving. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is automating routine tasks such as suturing and tissue dissection, aiming to further improve consistency and surgical outcomes [4] . Next-generation systems, such as the da Vinci 5 and Medtronic Hugo, are expanding the scope and accessibility of robotic-assisted procedures.
Human-robot collaboration is expected to deepen, with robots handling routine elements so surgeons can focus on critical, high-skill tasks [1] . As technology advances, it is likely that more procedures will become minimally invasive, leading to shorter hospital stays and improved patient satisfaction.
Alternative Approaches and Additional Resources
Some procedures may still be best performed using traditional open or laparoscopic surgery, particularly in cases with complex anatomy or where robotic systems are unavailable. Discuss all potential options with your healthcare provider, and consider the risks and benefits of each approach.
For those seeking more information, reputable resources include the American College of Surgeons, academic medical centers, and specialty societies. When searching for services, use official hospital websites and verified health system portals. Avoid relying on unofficial sources for medical decision-making.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Robotic technology is reshaping the landscape of healthcare surgery, delivering improved precision, reduced complications, and shorter recovery times for many patients. Access to these procedures typically involves consultation with specialists and verification of hospital capabilities and insurance coverage. While not suitable for every case, robotic-assisted surgery represents a significant advancement, and its role will continue to grow as technology matures. Patients are encouraged to stay informed, seek expert advice, and explore all available treatment options.
References
- [1] Reddy K. (2023). Advancements in Robotic Surgery: A Comprehensive Review. PMC.
- [2] Morris B. (2005). Robotic Surgery: Applications, Limitations, and Impact on Surgical Training. PMC.
- [3] Brainlab (2024). Types of Medical Robots in Use Today and in the Future.
- [4] American Hospital Association (2025). 3 Ways Robotic Surgery Is Changing Health Care This Year.
- [5] EBSCO (2024). Robotics in Healthcare.