Proven DIY Strategies to Keep Flood Water Out of Your Home
Understanding Flood Risk and Why DIY Matters
Flooding is one of the most common and expensive natural disasters homeowners face, and even a small amount of water intrusion can lead to significant property damage, mold growth, and costly repairs. Taking proactive, do-it-yourself steps can help reduce your home’s vulnerability to floodwaters. While professional flood-proofing offers strong protection, many effective measures are accessible for homeowners who want to act quickly and affordably. This guide explains actionable, evidence-based methods to keep floodwater out of your house, highlights common pitfalls, and provides step-by-step instructions for each strategy.
Seal Vulnerable Openings and Foundations
Floodwater often enters homes through small cracks, gaps, or poorly sealed areas in foundations, basements, windows, and doors. Sealing these entry points is a cost-effective, critical first line of defense. Begin by thoroughly inspecting the exterior and interior of your home, looking for any visible gaps or cracks. Use hydraulic cement, masonry caulk, or a high-quality waterproof sealant to close these areas. Make sure to cover both foundation cracks and any gaps around window and door frames. For added protection, apply waterproofing compounds to basement walls. These products create a barrier that significantly reduces water seepage during heavy rainfall or flooding events. Regularly check and maintain these seals, as weather and time can degrade their effectiveness [1] [2] .
Install and Maintain a Sump Pump System
One of the most effective DIY flood prevention tools is a sump pump . Installed at the lowest point of your basement or crawlspace, a sump pump collects water and automatically removes it from your home through a discharge pipe. To maximize protection:
- Choose a sump pump rated for your basement’s size and local water table conditions.
- Install a battery backup to ensure the pump works during power outages, which are common in storms.
- Test the pump regularly and keep the discharge line clear of debris.
- Consider a water alarm system for early warning.
If your home does not have a sump pump, you can hire a professional or follow manufacturer instructions for DIY installation. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the system operates during emergencies [2] [1] .

Source: smilepaso.com
Use Flood Barriers and Sandbags Effectively
Sandbags are a classic, widely available option for emergency flood defense. When used correctly, they can help direct water away from vulnerable doors and low windows. For best results:
- Keep a supply of sandbags (filled with sandy soil) stored in your garage or shed. Do not wait until flooding is imminent, as supplies may run out locally.
- Stack sandbags in a pyramid shape for stability and coverage.
- Place sandbags tightly together and stagger the layers to minimize gaps where water can seep through.
- After the flood threat has passed, dispose of used sandbags according to local regulations, as they may be contaminated.
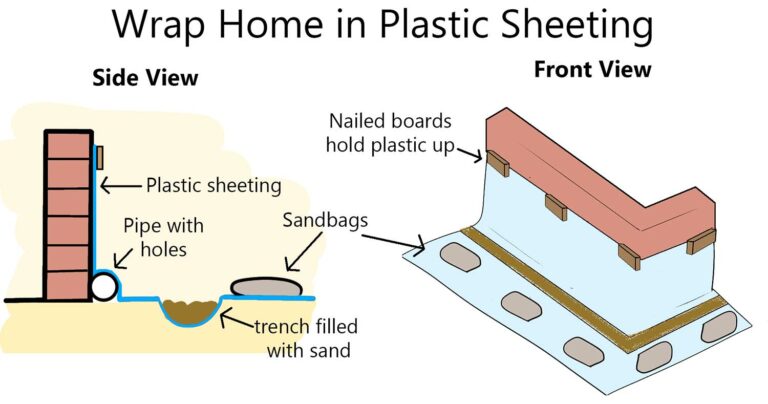
Alternative DIY barriers-such as plastic sheeting or plywood-can offer some protection when secured firmly across doors and windows. However, these makeshift options are generally less reliable than sandbags or commercial flood barriers, as they can allow water to seep through small gaps [5] [3] .
Improve Drainage and Landscaping Around Your Home
Your yard’s drainage design can have a major impact on how water interacts with your home’s foundation. Ensure that your lawn slopes away from the house, directing water toward the street or a designated drainage area. If you notice standing water or a slope toward your foundation, consider regrading the soil or installing French drains. Avoid placing mulch directly against your siding, as it can trap moisture and promote rot. Leave a gap of at least 6 inches between mulch and the house, and use strategic plantings to absorb excess rainwater. Clean gutters and downspouts regularly to prevent overflow and direct water at least 5-10 feet away from the foundation using downspout extenders [2] [4] .
Upgrade to Flood-Resistant Materials
Where possible, replace susceptible materials with flood-resistant alternatives. For example, swap out wood floorboards and carpets for ceramic tile, vinyl, or rubber flooring. Use moveable rugs instead of fitted carpets for easier cleaning and faster drying after a flood event. Consider using cement board or pressure-treated wood for walls and replacing wooden window frames with metal or composite options. These upgrades reduce long-term water damage and mold risk [1] .
Additional DIY Tips and Emergency Actions
During active flood threats, quick DIY actions can help minimize water entry:
- Add weather stripping around doors and windows to block wind-driven rain and shallow flooding.
- Apply extra caulking to any gaps that have developed around openings, especially before storm season.
- Use duct tape to seal appliance doors and wrap electronics in plastic to prevent water damage.
- Elevate electrical components, outlets, and appliances at least one foot above predicted flood levels. This should be done by a licensed electrician for safety.
Consider installing flood vents in crawlspaces or garages. These permanent openings allow water to flow through, preventing dangerous pressure build-up that can damage walls and foundations. Flood vents are especially recommended in high-risk zones and can often be retrofitted to existing homes [1] [4] .
Common DIY Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
While DIY flood protection can be highly effective, there are pitfalls to avoid:

Source: dashangu.com
- Relying solely on sandbags or makeshift barriers for severe, prolonged flooding-a combination of methods is best.
- Neglecting regular maintenance of sump pumps and seals.
- Using permeable materials (like burlap sacks) in high-risk scenarios; these allow water through and are less effective for total protection.
- Failing to address landscaping or gutter maintenance, which can undermine other efforts.
Combining multiple strategies-such as sealing, installing a sump pump, maintaining landscaping, and having sandbags on hand-yields the best results for most homes [3] .
Accessing Help and Additional Resources
If you require more advanced solutions or experience persistent flooding, you may benefit from professional waterproofing or consulting local emergency management agencies. To learn about flood risk specific to your area, you can visit the official FEMA website and search for “Flood Map Service Center.” For more information on disaster preparedness, contact your local government’s emergency management office. Many communities offer sandbag distribution and flood barrier programs during flood season; check with your city or county public works department for details. Home improvement stores and hardware retailers often stock sump pumps, waterproofing materials, and ready-to-use sandbags.
Key Takeaways and Next Steps
Protecting your home from floodwater is possible with the right combination of DIY strategies and ongoing maintenance. Focus on:
- Sealing cracks and vulnerable openings with appropriate waterproof materials.
- Installing and maintaining a reliable sump pump system.
- Using sandbags and other barriers effectively during emergencies.
- Improving yard drainage, keeping gutters clear, and maintaining the proper lawn slope.
- Upgrading to flood-resistant building materials where feasible.
- Consulting official resources and your local government for flood maps and preparedness programs.
With preparation and regular upkeep, you can greatly reduce your risk of costly flood damage and keep your home-and your peace of mind-intact.
References
- [1] FEMA (2020). Protect Your Home from Flooding Brochure.
- [2] Angi (2024). How to Keep Floodwater Out of Houses (DIY Guide).
- [3] Dam Easy (2023). DIY Flood Barrier Solutions: Weighing the Options.
- [4] HowStuffWorks (2024). Is there a way to keep floodwaters out of the house?
- [5] Hippo (2022). How to Keep Floodwater out of Your House to Protect Your Property.